Overview
Squatters in Illinois have rights that can pose challenges for property owners. This guide covers everything landlords need to know to protect their investments, from squatter's rights to eviction laws and preventive measures.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
- What squatters’ rights are in Illinois
- The legal framework of adverse possession
- How to legally remove squatters
- Steps landlords can take to prevent squatting
By understanding these rights, property owners can take proactive steps to avoid legal disputes and safeguard their properties.
Understanding Squatter's Rights in Illinois
In Illinois, squatting refers to occupying a property without the owner’s permission. Under certain conditions, squatters can gain legal rights, including ownership, through adverse possession laws. Common scenarios include:
- Occupying abandoned or foreclosed properties
- Misunderstandings regarding property boundaries
- Unforeseen emergencies leading to temporary shelter
To claim rights, squatters must meet Illinois’ legal requirements, such as continuous occupancy for 20 years. Property owners should stay vigilant and act quickly to address unauthorized occupancy. For more information, visit the Illinois General Assembly.
Adverse Possession in Illinois
Adverse possession allows squatters to claim ownership of a property after meeting specific legal requirements. In Illinois, these include:
- Hostility: The squatter occupies the property without permission.
- Actual Possession: The squatter lives on and maintains the property.
- Open and Notorious: The occupation is obvious and not hidden.
- Exclusive and Continuous: The squatter lives on the property solely for at least 20 years.
Property owners should regularly inspect and maintain their properties to prevent squatters from meeting these requirements. Learn more from the Illinois Department of Revenue.
Eviction Process for Squatters
Evicting squatters in Illinois requires following the state’s legal eviction process. Steps include:
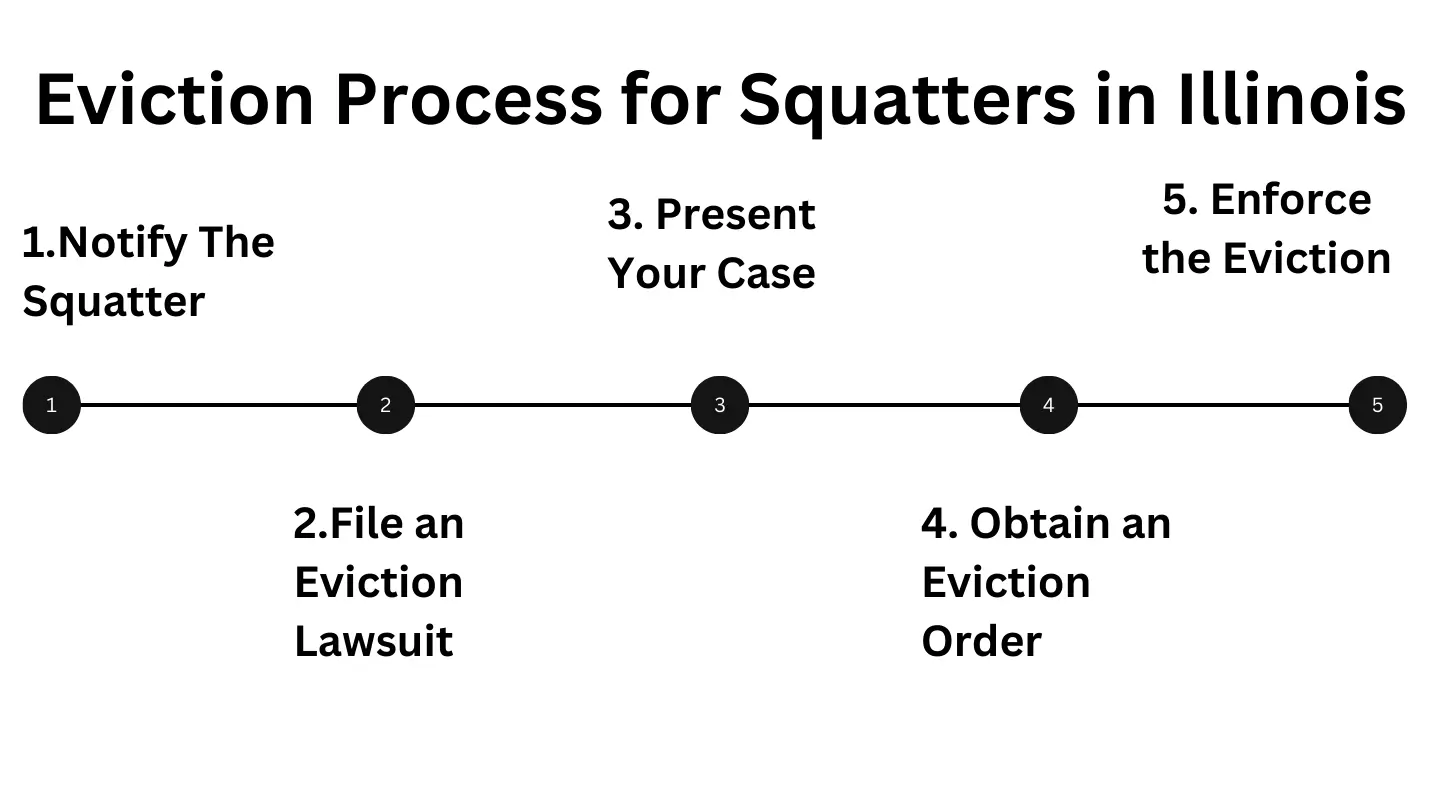
- Notify the squatter with a formal eviction notice.
- File an eviction lawsuit if they refuse to leave.
- Present your case in court and obtain an eviction order.
- Work with law enforcement to enforce the eviction.
Avoid taking matters into your own hands, as this can lead to legal complications. Always follow the proper legal channels. Refer to the Illinois Courts for details.
Tips to Prevent Squatters
Preventing squatters requires vigilance and proactive measures, such as:
- Paying property taxes to maintain ownership records.
- Installing security systems to deter unauthorized entry.
- Conducting regular property inspections.
- Posting “No Trespassing” signs on vacant properties.
- Hiring property management services for oversight.
These steps can help you safeguard your property and avoid potential legal disputes with squatters. For property record verification, visit the Cook County Recorder of Deeds.
Frequently Asked Questions
Final Thoughts
Understanding Illinois squatter's rights is crucial for property owners to protect their investments and navigate potential disputes. By staying informed about adverse possession laws and eviction procedures, landlords can take proactive measures to safeguard their properties against unauthorized occupants.
At Simpli Management, we empower landlords with tools like our Property Valuation Software to manage properties effectively and address challenges like squatting. Explore our property management solutions today.